开始之前
文章转自Spring IOC 容器源码分析。
基本就是里头的东西,只不过自己跟着在源码中转了一遍,会有一点点不一样。
源码版本信息
- spring-context: 5.1.5.RELEASE
节省篇幅起见,删掉了源码中打印日志相关的代码。
一个简单的开始:ApplicationContext
1 | |
其中 ApplicationContext 是Spring中配置应用的核心接口,继承了多个接口,使其拥有了众多功能:
ListableBeanFactory,赋予了它Bean工厂的能力;ResourceLoader,赋予了它加载文件资源的能力;ApplicationEventPublisher,赋予了它向注册的监听器发布事件的能力;MessageSource,赋予了它处理消息,支持国际化的能力;- 各上下文类成“父子”关系,“子”上下文中的定义优先于“父”上下文的,一整个web项目都可以用一个上下文,而其下的每一个servlet都可以有自己的上下文
在上面代码中,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext是在类路径中寻找xml格式的配置文件,然后根据其内容构建应用上下文。其大致的继承结构如图所示:
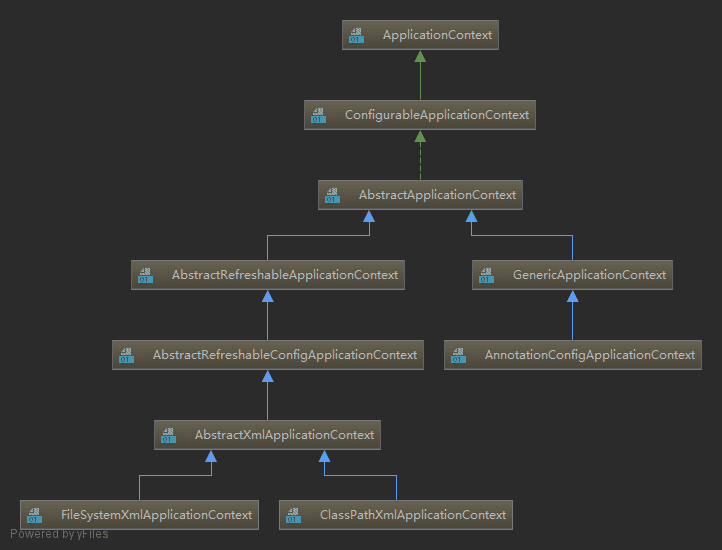
该树的三个叶节点分别是:
FileSystemXml...:从系统路径中找xmlClassPathXml...:从类路径找xmlAnnotationConfig...:根据注解配置
现在加点实际的东西。
通过上下文容器,来获得一个对象。
首先定义一个接口及其实现类
1 | |
然后是配置文件application.xml
在项目目录的resources下新建一个application.xml,内容如下:
1 | |
然后在程序中使用上下文来获取对象实例并调用其接口
1 | |
例子很简单,原理就复杂了,下面将分析Spring是如何通过配置文件启动ApplicationContext,并在启动过程中创建Bean,注入依赖等。
BeanFactory简介
在上文对ApplicationContext的介绍中,我们知道ApplicationContext继承了ListableBeanFactory接口,使其拥有了Bean工厂的能力,换句话说,ApplicationContext就是一个BeanFactory。
先来看一下BeanFactory的继承关系:

- 顶层的
BeanFactory都是一些基本的、获取单个Bean的方法; - 第二层的
ListableBeanFactory,主要提供了一些获取多个Bean的方法;HierarchicalBeanFactory,顾名思义,提供了将多个BeanFactory设为“父子”关系的方法;AutowireCapableBeanFactory,提供了自动装配Bean的能力; ApplicationContext,我们的主角,继承了第二层的中的两个,没继承的那个,也通过方法getAutowireCapableBeanFactory()持有了;ConfigurableListableBeanFactory继承了第二层中的所有接口,也是个特殊的接口,先提一嘴;- 其它的类就不一一提了。
启动过程分析
先从ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的构造方法说起:
1 | |
其中核心方法是refresh(),之所以叫refresh而不是init之类的,是因为在ApplicationContext建立起来之后,
是可以通过该方法重建的:销毁原有的,建立新的。
refresh()
AbstractApplicationContext.java
1 | |
创建容器前的准备工作:prepareRefresh()
AbstractApplicationContext.java
1 | |
注册Bean到工厂中:obtainFreshBeanFactory()
AbstractApplicationContext.java
1 | |
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext.java
1 | |
到这里其实可以看到,虽然前面提到说 ApplicationContext继承了两个 BeanFactory接口,
但是其本身不实现相应的方法,而是通过(委托)内部持有的 DefaultListableBeanFactory来完成BeanFactory相关的操作。
为啥是 DefaultListableBeanFactory?此处再看一下BeanFactory的继承树:

DefaultListableBeanFactory在图中最下方,实现了可见的所有接口,功能最全。
如果你想要在程序运行的时候动态往 Spring IOC 容器注册新的 bean,就会使用到这个类。那我们怎么在运行时获得这个实例呢? 之前我们说过 ApplicationContext 接口能获取到 AutowireCapableBeanFactory,就是最右上角那个,然后它向下转型就能得到 DefaultListableBeanFactory 了。
在进一步向下之前,我们需要了解一下什么是BeanDefinition。上文提到,将Bean注册到BeanFactory,
可以简单理解为是一个完成 BeanName 到 BeanDefinition 的Map过程,这里的 BeanDefinition 保存了 Bean 的信息,
比如这个 Bean 指向的是哪个类、是否是单例的、是否懒加载、这个 Bean 依赖了哪些 Bean 等等。
简单来说,Bean和BeanDefinition 类似于 实例和类的关系吧。
BeanDefinition定义
1 | |
众多依赖信息,先求个眼熟。但是可以看到,里头并没有getInstance之类的方法来获取实例,这点后面会说。
介绍完 BeanDefinition,再回到之前的refreshBeanFactory方法。
在有一个BeanFactory之后,还有两步要走:
1 | |
先看第一个:
customizeBeanFactory
这个比较简单,就是设置两个Boolean值
1 | |
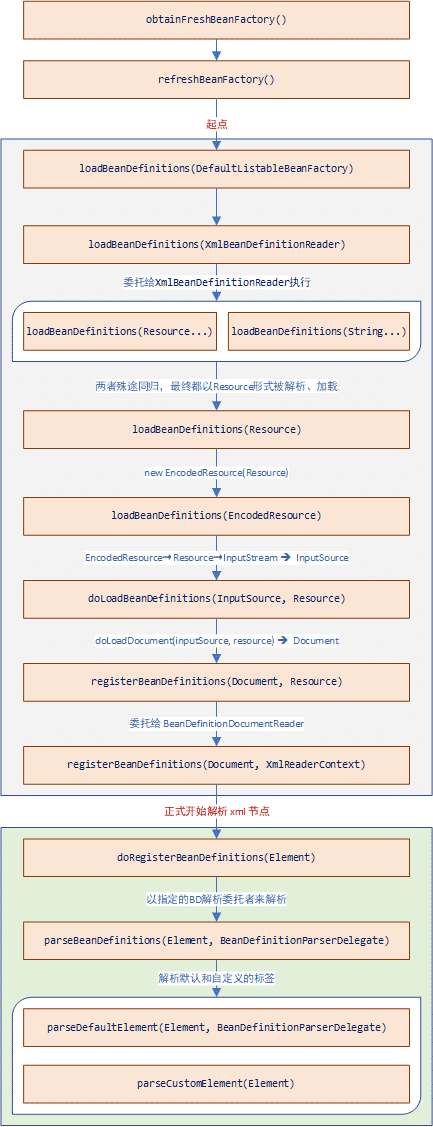
重头戏:loadBeanDefinitions
AbstractXmlApplicationContext.java
1 | |
AbstractBeanDefinitionReader.java
1 | |
XmlBeanDefinitionReader.java
1 | |
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
1 | |
可以看到解析BeanDefinition分成两种:
- Default Element: 即
xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"下的四个标签<import />、<alias />、<bean />和<beans /> - Custom Element: 其他标签,如我们经常会使用到的
<mvc />、<task />、<context />、<aop />等。
如果要解析这些非Default的标签,就要在XML头部引入相应的namespace及.xsd的文件路径,如下所示,同时代码中需要提供相应的 parser 来解析, 如 MvcNamespaceHandler、TaskNamespaceHandler、ContextNamespaceHandler、AopNamespaceHandler 等。
1 | |
回头再看看处理default标签的方法:
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
1 | |
在解析<bean />前,回顾一下Bean都有哪些属性
- class
- name:可指定 id、name(用逗号、分号、空格分隔)
- scope
- constructor-arg
- properties
- autowiring mode:no(默认值)、byName、byType、 constructor
- lazy-initialization mode:是否懒加载(如果被非懒加载的bean依赖了那么其实也就不能懒加载了)
- initialization method:bean 属性设置完成后,会调用这个方法
- destruction method: bean 销毁后的回调方法
这些属性其实就是与BeanDefinition这个类里出现过的get/set方法对应的。例子如下:
1 | |
回到解析<bean />的方法中:
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.java
1 | |
来看看是怎么根据配置文件来生成BeanDefinition实例的
1 | |
到此,完成了一个<bean />到 BeanDefinitionHolder,回到解析<bean />的方法上:
DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader.java
1 | |
这个时候我们已经有了一个BeanDefinitionHolder,里头有:
1 | |
先来看看怎么注册Bean:
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.java
1 | |
DefaultListableBeanFactory.java
1 | |
OK,到这里为止,已经注册了各bd,并发送了注册事件。下面我们来看看refresh的第3步:
准备Bean容器prepareBeanFactory
AbstractApplicationContext.java
1 | |
初始化所有的 singleton beans:finishBeanFactoryInitialization
到目前为止,应该说 BeanFactory 已经创建完成,并且所有的实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口的 Bean 都已经初始化,
并且其中的 postProcessBeanFactory(factory) 方法已经得到回调执行了。
而且 Spring 已经“手动”注册了一些特殊的 Bean,如 environment、systemProperties 等。
(这里我们跳过了refresh中的一大段,直接进入重点关注对象)
AbstractApplicationContext.java
1 | |
DefaultListableBeanFactory.java
1 | |
接下来讲一下getBean()
AbstractBeanFactory.java
1 | |
接下来要讲的是createBean方法:
AbstractBeanFactory.java
1 | |
第三个参数args就是要给构造器或FactoryBean的参数,但是在初始化Singleton时,传的是null。
这回要用到一个新的类AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java,顾名思义,和自动注入有关,主要为了以下场景:
1 | |
1 | |
这是一种混用的场景,Spring会自动处理这种情况。知道这回事就行,继续向前:
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
1 | |
doCreateBean()
1 | |
到此为止,已经说完了整个初始化过程,再来讲一下doCreateBean方法中的三个方法:
- createBeanInstance,创建实例
- populateBean,依赖属性注入
- initializeBean,回调方法
先看创建实例的方法:
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
1 | |
SimpleInstantiationStrategy.java
1 | |
再看看依赖属性注入的方法:
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
1 | |
最后讲讲回调处理:
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory.java
1 | |
总结
加载BeanDefinition
加载BeanDefinition是注册Bean到工厂中的关键方法,其大致调用流程如下图所示: