本文主要介绍JDK8中的HashMap中的get()、put()和resize()方法。
一、几个常量值
先介绍一下在源码中常见到的几个常量值。
1 | |
二、构造方法
HashMap 中一共有4种构造方法,列举如下:
注意:
除了第4个以其它map作入参的构造方法外,其余的都不初始化table数组!
初始化工作是在put第一个元素时完成的。
1 | |
三、get方法
1 | |
3.1 getNode()
1 | |
3.2 hash()
这里顺带一提 jdk8 中 HashMap 的 hash()方法实现:
- key 为null,则为0,因此
put(null, obj)时,都放在数组的第一个位置; - 高低16位异或,称为hash扰动,低16位保留高16位的信息,减少冲突
1 | |
四、put方法
1 | |
4.1 putVal()
1 | |
4.2 treeifyBin()
这个方法不细讲,只是提一下树化的另一个条件(在几个常量中介绍过):
tab.length >= MIN_TREEIFY_CAPACITY
1 | |
4.3 put 小结
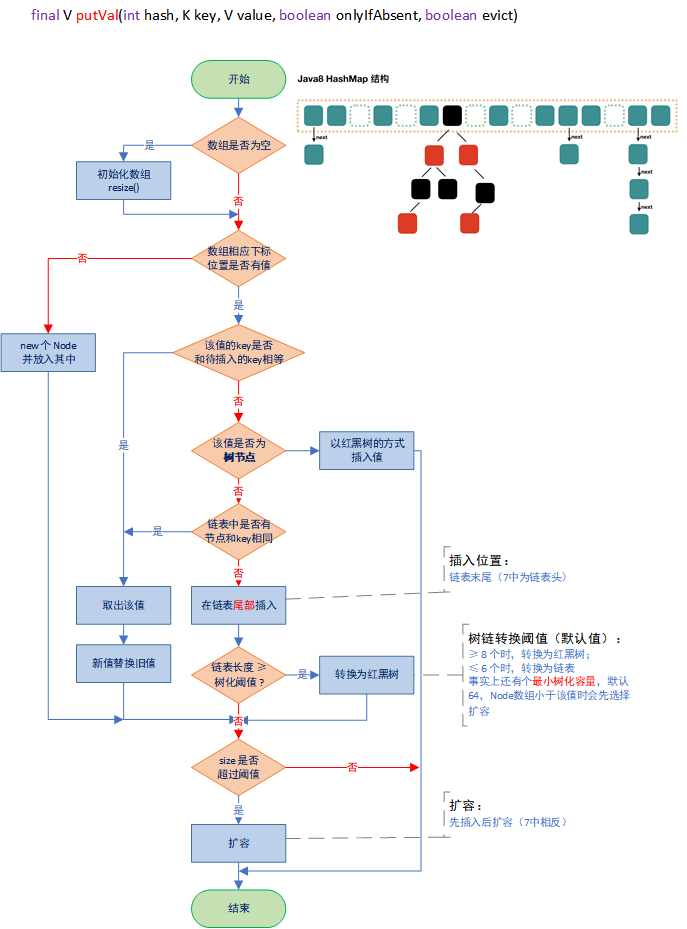
可以看到put过程中有以下几种情况:
- 数组的指定下标位置还为null
- 数组的指定下标位置不为null,但是头节点就和待插入值就相同
- 数组的指定下标位置不为null,头节点也不一样,而且是个红黑树节点
- 数组的指定下标位置不为null,头节点也不一样,而且是个正常的链表
- 链表里不存在key相同的,则添加到链表尾(JDK7 中是添加到链表头)
- 链表内存在相同key,则替换
还有两点需要注意的是:
- 先插入,后检查是否需要扩容;
- 并不是达到树化阈值就要树化。
put 的流程图如下:
五、resize方法
1 | |
在resize时,新的Node数组长度是原先的2倍。 由于长度都是2的指数,以及hash的特点,原数组中节点的要么在原地保留,要么移动到 (原位置 + 原数组长度) 的地方:
假设原数组长度为oldCap = 16,扩容后newCap = 32;
某Node节点的hash值为h的末5位为10101,则 h&(oldCap-1) = 0101,在下标为5的槽位;
扩容后,h&(newCap-1) = 10101,在下标为(5+16 = 21)的槽位。
由于这个特性,扩容后每个Node链表中,有一部分需要到新的下标位置,一部分还在原来的下标位置。
所以这里用了lo和hi两个链表,来分别存放这两部分数据。然后一把把这些数据迁移到新的数组中。
–over–