相关链接:JDK8中 HashMap 源码简析
本文主要介绍JDK8中ConcurrentHashMap的get()、put()方法,其中put()方法涉及到扩容,较为复杂,需要用心看下。
一、几个常量值
相对HashMap,ConcurrentHashMap 多了很多常量,这里先罗列一些,混个眼熟,后面用到的再细讲。
这几个和HashMap是一样的,不再赘述。
1 | |
这几个是 ConcurrentHashMap 独有的:
1 | |
一头雾水?那就对了,先有个眼熟,往下接着看。
二、几个Node内部类
ConcurrentHashMap 里有几个Node的子类,分别表示几种不同状态下的节点。如图所示:
这里的状态就是上面常量中的那几个MOVED/TREEBIN/RESERVED。
2.1 Node:普通的节点
Node是常规链表状态下的节点
1 | |
2.2 TreeNode:红黑树节点
1 | |
2.3 TreeBin:持有红黑树根节点的一个东东
TreeBin 不保存 key 和 value ,而是持有红黑树的根节点;它的hash值是TREEBIN(-2)
1 | |
2.4 ForwardingNode:代表数据正在迁移
ForwardingNode 代表正在迁移数据(扩容中),持有扩容后的table表;它的hash值是MOVED(-1)
1 | |
2.5 ReservationNode:占位节点
computeIfAbsent 和 compute 方法中用到的占位节点,hash值为RESERVED(-2)
1 | |
仍然是眼熟阶段,继续向下。
三、get方法
1 | |
spread()是 ConcurrentHashMap 中的hash计算方法
- 和HashMap一样的是:同样需要高低位扰动(spread);
- 不一样的是:1、没有对key为null的处理;2、和HASH_BITS与后确保符号位为0;
1 | |
四、put方法
1 | |
4.1 putVal方法
1 | |
可以看到,put时有4种情况:
- 数组还为null,需要初始化;
- 数组指定下标值为null,则CAS插入;
- 数组指定下标的节点正在迁移,则帮忙数据迁移;
- 正常的插入值。
整个过程是自旋的,不成功插入不退出。
先来看看初始化数组的方法。
4.2 initTable()
插入第一个节点时,需要初始化table数组。
比较简单,有别的线程在初始化就等一会,不然就自己开干。
1 | |
4.3 treeifyBin()
树化的方法。
1 | |
高能预警!!!下面两个方法(扩容和数据迁移)是JDK8 ConcurrentHashMap的难点所在。
4.4 tryPresize()
有两个地方会调用这个方法:
- putAll()方法,被put的数量不定;
- treeifyBin(),此时是扩容,size必是2的指数
1 | |
4.5 transfer()
1 | |
4.6 helpTransfer()
1 | |
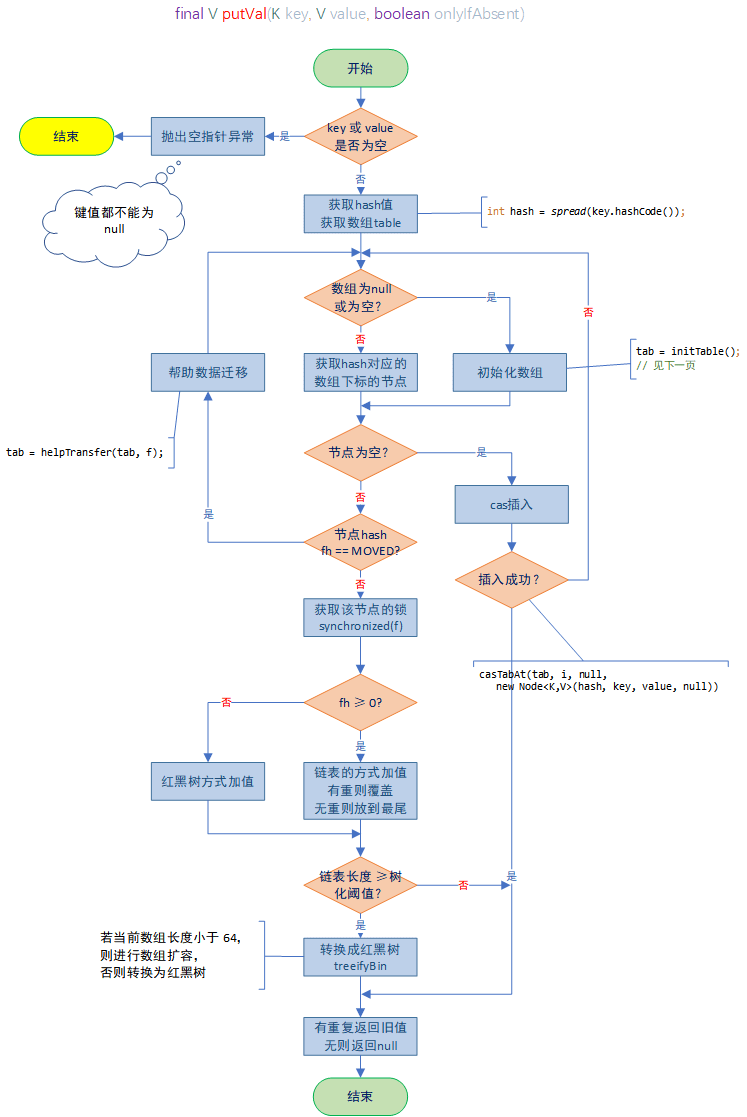
最后放一张put的简易流程图:
– over –